



Next: Definition 3: Non-frequentist subjective
Up: How is probability defined?
Previous: Definition 1: Number of
Contents
For repeated events, probability can be estimated by the ``long-run''
relative frequency of an event out of a set of many trials.
If an event occurs 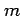 times in
times in 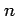 trials then the relative frequency
trials then the relative frequency
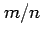 provides an unbiased estimate of the probability of the event.
In the asymptotic limit as the number of trials
provides an unbiased estimate of the probability of the event.
In the asymptotic limit as the number of trials 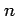 tends to infinity,
the relative frequency converges to the true probability of the event
(``Law of large numbers''). This interpretation involving repeated
trials is known as the ``frequentist'' approach to probability.
tends to infinity,
the relative frequency converges to the true probability of the event
(``Law of large numbers''). This interpretation involving repeated
trials is known as the ``frequentist'' approach to probability.
David Stephenson
2005-09-30