Following the ideas of Krassowska and Neu [1994] we will now simplify this extensive nonlinear system of partial differential equations; note that in the electric part of the equations, all the nonlinearity is located in the term f(), and the remaining linear problem can be (in principle) solved. Summing the Eqs. (7) and (8), we get a linear equation
for the overall current balance of the membrane element, which, together with the equations
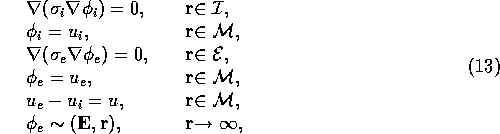
constitute a well posed elliptic problem for finding ![]() and
and
![]() at given
at given ![]() and u. Differentiation of
(10) by time and substituting into (7) or
(8), together with the slow equations, yields then the
resulting system of equations of the form
and u. Differentiation of
(10) by time and substituting into (7) or
(8), together with the slow equations, yields then the
resulting system of equations of the form
where u, v and w are now functions of time and position on the
membrane, ![]() is a linear (generally, integro-differential) operator in
a space of scalar functions on the membrane, and
is a linear (generally, integro-differential) operator in
a space of scalar functions on the membrane, and ![]() is a linear
operator mapping vectors
is a linear
operator mapping vectors ![]() to scalar functions on the membrane. The
specific forms of
to scalar functions on the membrane. The
specific forms of ![]() and
and ![]() depend on the geometry of
depend on the geometry of ![]() and on the coefficients
and on the coefficients ![]() and
and ![]() . We use the
following properties of these operators:
. We use the
following properties of these operators:
These properties follow from the derivation of (14). ![]() represents the currents between different loci of membrane, both through
interior and exterior domains, and
represents the currents between different loci of membrane, both through
interior and exterior domains, and ![]() is the additional current
due to the external field.
is the additional current
due to the external field.