



Next: Example 3: Normal (Gaussian)
Up: Theoretical continuous distributions
Previous: Example 1: Uniform distribution
Contents
A positive random variable is exponentially distributed
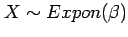 when
when
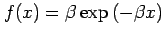 for
for 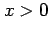 and
and 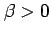 .
In other words, the random variable is more likely to take
small rather than large positive values.
The single parameter,
.
In other words, the random variable is more likely to take
small rather than large positive values.
The single parameter, 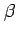 , fully determines the exponential
distribution and all its moments, for example,
, fully determines the exponential
distribution and all its moments, for example,
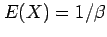 and
and
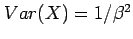 .
.
David Stephenson
2005-09-30