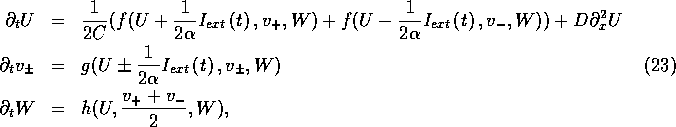
The generalization of equations (19) for spatially extended tissue is straightforward as the deviation of each individual cell from an isopotential state takes place only during the short time periods of external stimulation, and outside these periods cable theory gives
where U, ![]() and V are now functions not only of time t,
but also of distance along the fibre x, and the diffusion coefficient
for voltage, D, is proportional to the intercellular conductivity.
and V are now functions not only of time t,
but also of distance along the fibre x, and the diffusion coefficient
for voltage, D, is proportional to the intercellular conductivity.
![]() gives a conduction velocity of about
350 mm/s for a solitary wave through resting tissue. The value of D is
necessary only for the interpretation of spatial scales as equations
(23) are invariant under simultaneous change of spatial
scales and coefficient D.
gives a conduction velocity of about
350 mm/s for a solitary wave through resting tissue. The value of D is
necessary only for the interpretation of spatial scales as equations
(23) are invariant under simultaneous change of spatial
scales and coefficient D.